Introduction: The Chocolate Crisis No One Saw Coming
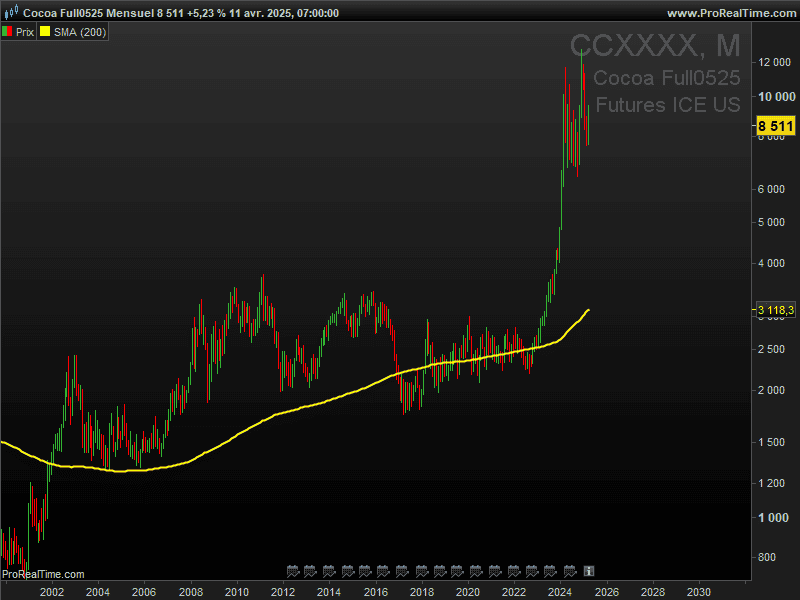
In early 2024, the world’s sweet tooth met a bitter reality: cocoa prices hit an all-time high of over $12,000 per metric ton, a stunning 400% increase in just three years. Behind the headlines of shrinking chocolate bars and skyrocketing Easter egg prices lies a complex storm of climate change, geopolitical friction, and financial speculation.
For savvy investors, this isn’t just a story of supply chain pain it’s an extraordinary opportunity. As the cocoa market enters uncharted territory, traders on platforms like eToro are exploring how to position themselves for profits.
This article unpacks:
- The root causes behind the cocoa price surge
- Whether prices will stay high or come crashing down
- How you can invest in cocoa through eToro ($Cocoa), even without owning physical beans
Below is a chart of the Cocoa Futures (CC ICE) illustrating the surge in cocoa prices over the past 25 years.
Part 1: The Supply Crisis That Broke the Market
West Africa: Ground Zero of the Cocoa Crunch
Over 70% of the world’s cocoa comes from just two countries: Ivory Coast and Ghana. In recent years, these agricultural powerhouses have faced a brutal combination of climate disasters:
- Torrential rains triggered black pod rot, a fungal disease that can destroy up to 40% of a harvest.
- Followed by severe drought, the result is the smallest harvests since 1954.
- Meanwhile, 60% of cocoa trees are now over 20 years old and well past peak productivity.
Replanting costs are high ($3,000 per acre) and trees take 5 years to mature, meaning no quick fix for supply.
Geopolitics and Fertilizer Shocks
The Russia-Ukraine war sent fertilizer prices soaring by 180%, making cocoa cultivation less profitable. Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire have also imposed a $400/ton “sustainability fee” to support farmers noble, but it’s sparked a smuggling boom of over 200,000 tons annually into neighboring countries without the tax.
Part 2: The Demand Surge and Financial Frenzy
Chocolate Giants in Panic Mode
Demand for chocolate keeps growing, especially in India, China, and Brazil. But with input costs spiking, global chocolate makers like Nestlé ($NESN.ZU), Hershey, and Mondelez are responding with:
- Shrinkflation smaller bars for the same price
- Reformulation using cheaper cocoa substitutes
- Price hikes up over 22% in 2024 alone
The industry is bracing for profit margin compression or consumer backlash, or both.
Wall Street’s Cocoa Frenzy
Hedge funds now hold over $8 billion in cocoa long positions, treating cocoa as a speculative vehicle. The paper market dwarfs the physical one, with only 3 days’ worth of real-world supply in exchange warehouses.
At the height of the rally, 80% of cocoa futures were held by traders who would never see a real cocoa bean. The massive disconnect between speculation and supply helped turbocharge prices into record territory.
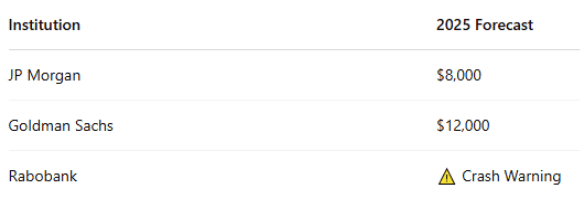
Part 3: Will the Cocoa Boom Continue?
What’s Next for Cocoa Prices?
Whether the rally holds or unravels depends on a handful of unpredictable variables:
Bullish Drivers
- Prolonged El Niño continues to hinder yields
- No rapid recovery in West African output
- Institutional speculators still heavily long cocoa
Bearish Risks
- R&D breakthroughs in synthetic cocoa (Mars Inc. is investing $1B)
- Rising chocolate prices triggering a consumer boycott
- Potential government interventions (price caps, export controls)
Part 4: How to Invest in Cocoa via eToro
Even without access to traditional futures markets, eToro offers powerful tools for retail investors to gain cocoa exposure. Here’s how to build your cocoa play:
1. Cocoa Futures CFDs (Trade the Price Directly)
eToro offers CFD contracts (Contracts for Difference) on ICE Cocoa Futures ($Cocoa), which mirror the price of real cocoa without the need to take delivery.

Why CFDs?
- Go long or short on cocoa
- Use leverage (cautiously!)
- Trade during major volatility events (e.g., grinding season in March/July)
✅ Pros: High exposure, flexible trading
❌ Cons: Leverage amplifies risk use strict risk controls
2. Cocoa-Linked Stocks on eToro
Another way to tap into cocoa’s rise is to invest in companies that process, buy, or depend on cocoa. eToro makes it easy to buy shares or fractional stocks in these companies.
Cocoa-Exposed Companies:


🟢 Bullish on cocoa processors like Callebaut → profit from strong margins
🔴 Bearish on chocolate retailers like Hershey → hurt by cost pressures
✅ Pros: Familiar investment format
❌ Cons: Share price driven by broader business performance, not just cocoa
3. Commodity ETFs & Agriculture Indices
While there’s no cocoa-only ETF on eToro, you can get indirect exposure through:
- Invesco DB Agriculture Fund (DBA)
- WisdomTree Agriculture ETF

These funds hold cocoa, coffee, sugar, and other softs ideal if you want diversification within the agri-commodity space.
✅ Pros: Lower volatility
❌ Cons: Less pure-play cocoa exposure
Risk Management: Cocoa Is Not for the Faint-Hearted
Cocoa is one of the most volatile commodities, with weekly swings of 25-30% in 2024 alone. Before trading, consider these critical risks:
1. Extreme Volatility
- Prices can surge or crash rapidly due to weather shocks, disease outbreaks (e.g., swollen shoot virus), or speculative trading.
- Liquidity gaps can worsen slippage, especially during news events.
2. Geopolitical & Supply Chain Risks
- Over 70% of global cocoa comes from West Africa (Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana), where political instability, export restrictions, or child labor scandals can disrupt supply.
- Climate change exacerbates droughts and irregular rainfall, reducing yields long-term.
3. Leverage & Margin Risks
- Trading cocoa with leverage (e.g., CFDs, futures) can amplify losses beyond your initial deposit.
- Margin calls may force premature liquidation during drawdowns.
4. Currency & Macroeconomic Factors
- Cocoa is priced in USD; a strong dollar can depress demand from foreign buyers.
- Inflation, interest rate shifts, and recessions alter discretionary spending on chocolate.
5. Market Manipulation & Speculative Bubbles
- Hedge funds and algorithmic traders can exaggerate price swings, creating false breakouts.
- Example: The 2024 rally to $12,000/ton was partly driven by speculative positioning rather than fundamentals.
6. Regulatory & Exchange Risks
- Exchange rules (ICE, NYSE Liffe) can change margin requirements or halt trading during extreme moves.
- Governments may impose export bans (e.g., Ivory Coast’s 2022 temporary suspension).
7. Psychological Risks
- Emotional trading (FOMO during rallies, panic selling in crashes) often leads to poor timing.
- Overtrading due to cocoa’s volatility can erode capital via fees and spreads.
Here’s how I would approach it if I were to trade cocoa:
- I would limit cocoa to 3-5% of my portfolio to avoid overexposure
- I would set hard stop-losses (using eToro’s platform tools) to control risk
- I might hedge with coffee, sugar or gold to balance my positions
- I would consider taking profits near key levels (14k or 16k) if the market showed signs of reversing
Pro Tips for eToro Traders
- Set price alerts for El Niño updates and crop reports
- Watch West Africa radar maps (Zoom Earth)
- Follow market sentiment via eToro’s social feed
- Read earnings calls of Barry Callebaut and Lindt for supply/demand insight
Final Verdict: Cocoa Is Volatile Gold
In a world addicted to chocolate, cocoa has gone from a quiet commodity to a headline-grabbing market disruptor. The current rally isn’t just a blip, it’s the culmination of decades of underinvestment, climate collapse, and geopolitical friction.
Through platforms like eToro, everyday investors can now trade cocoa just like the pros via CFDs, stocks, and commodity ETFs.
Is Now the Time to Buy?
Green Light If You:
✔ Understand volatility
✔ Watch climate/weather patterns
✔ Can afford to risk a small % of portfolio
Red Light If You:
✖ Need stable, safe returns
✖ Can’t manage high-leverage products
✖ Think chocolate is recession-proof
“Cocoa has turned into a battlefield for traders. Those who survive the swings will taste sweet returns.” — Veteran ICE Trader
This communication is for information and education purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, a personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to buy or sell, any financial instruments. This material has been prepared without taking into account any particular recipient’s investment objectives or financial situation and has not been prepared in accordance with the legal and regulatory requirements to promote independent research. Any references to past or future performance of a financial instrument, index or a packaged investment product are not, and should not be taken as, a reliable indicator of future results. eToro makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this publication.



