Currency trading, or ‘forex’ trading as it is often called, has become immensely popular in recent years. It’s not hard to see why. Not only have advances in technology made it much easier for retail traders to access the currency market, but innovative new trading tools have also made it possible to start trading currencies with just a small amount of capital.
Interested in learning more about currency trading? This guide to currency trading is a great place to start. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the basics of currency trading and explain how you can trade the world’s currencies through eToro.
What is currency trading?
Currency trading is the process of buying and selling currencies such as the US Dollar, the Euro, and the British Pound.
Often called foreign exchange (forex) trading, it involves purchasing one currency while simultaneously selling another, with the aim of generating profits from currency movements.
In the past, currency trading was mainly carried out by banks, institutional investors, and hedge funds. However, thanks to advances in technology, literally anyone can trade currencies today.
Currency trading takes place on the foreign exchange market – a global marketplace in which traders all over the world trade currencies. This market is the largest financial market in the world, with around $5 trillion in currencies traded every day.
Trading currencies through eToro is straightforward. eToro’s trading platform is easy to use and has been designed to give traders the best chance of success.
The 10 most traded currencies in the world
| Currency | Symbol |
| US Dollar | USD |
| Euro | EUR |
| Japanese Yen | JPY |
| Pound Sterling | GBP |
| Australian Dollar | AUD |
| Canadian Dollar | CAD |
| Swiss Franc | CHF |
| Chinese Renminbi | CNH |
| Hong Kong Dollar | HKD |
| New Zealand Dollar | NZD |
Even if you have never actively traded currencies before, you’ve probably had some experience buying and selling currencies. For example, if you’ve taken a holiday abroad, you most likely swapped your home currency for an international currency. By exchanging one currency for another, you essentially participated in the foreign exchange market.
The benefits of currency trading
Currency trading is popular because it offers a number of benefits. Here’s a look at some of the main benefits:

Low capital requirements
One of the main attractions of currency trading is that you don’t need to have a lot of money to get started. This means that small investors can easily enter the market.
At eToro, the minimum deposit to start trading currencies is just $200.
A small deposit can go a long way
The reason you don’t need a lot of capital to start trading currencies is that it’s possible to use ‘leverage’ to control a large amount of money with just a small deposit. The way leverage works is that you essentially borrow money from your broker to trade with more money than you have deposited in your account.
eToro currently offers retail investors leverage of up to x30 for major currency pairs. This means that you can potentially trade $30 for every $1 that is in your account.
Transaction costs are low
Another benefit of currency trading is that transaction costs are low. Typically, there are no transaction fees on currency trades. The main form of fee that traders pay is the spread between the buy and the sell price of the trade (more on this later).
You can trade whenever you like
Finally, another big advantage of currency trading is that you can trade on your own schedule. The foreign exchange market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week. Trading begins with the opening of the Sydney session on Monday morning and closes with the New York session on Friday evening, which means there’s plenty of time to trade.
How does currency trading work?
The way currency trading works is relatively simple. When you trade currencies, you’re betting on the value of one currency relative to another.
Currency pairs
All currencies are traded in pairs. An example of a currency pair is GBP/USD. This particular currency pair reflects the British Pound to US Dollar exchange rate, or the number of US Dollars to one British Pound.
In a currency pair, the first currency is known as the ‘base’ currency and the second is known as the ‘counter’ currency or ‘quote’ currency.
Going long or short
Once you have chosen the currency pair that you want to trade, the next step is to decide whether the base currency is going to strengthen or weaken against the counter currency, and take a position accordingly.
If you believe that the base currency is going to strengthen against the counter currency, you buy (or ‘go long’) the currency pair. If you think that the base currency is going to weaken against the counter currency, you sell (or ‘go short’) the currency pair.
So for example, if you believe that the British Pound will strengthen against the US Dollar, you buy GBP/USD. Alternatively, if you think the British Pound will weaken against the US Dollar, you sell GBP/USD.
Profit and loss
Your profit or loss will depend on the extent to which you get your prediction right.
In currency trading, profits are measured in ‘pips.’ A pip is the smallest move a currency can make. In a currency pair that is priced to four decimal places such as GBP/USD, a pip is a price movement of 0.0001. If you buy GBP/USD at 1.2500 and close the trade at 1.2510, your profit is 10 pips.
The monetary value of your profit or loss will depend on how much money was risked on the trade and the amount of leverage used.
What drives currency movements?
A currency’s strength is affected by supply and demand dynamics. If demand for a currency increases, its value will rise. However, if demand decreases, its value will fall.
There are a number of factors that can influence supply and demand for a currency. Here’s a look at some of the main factors:
Interest rates
A country’s interest rates have a major impact on supply and demand for its currency. If a country increases its interest rates, demand for its currency tends to increase as foreign capital flows into the country. However, if a country lowers its interest rates, demand for its currency tends to fall as foreign capital flows out of the country.
Inflation
A country’s rate of inflation (the gentle increase in the prices of goods and services over time) can also impact supply and demand for its currency. A high inflation rate can lead to reduced demand.
Economic performance
Countries that are economically strong tend to see increased demand for their currencies. Conversely, countries that are experiencing economic challenges tend to see decreased demand for their currencies.
Some economic indicators that currency traders often monitor include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): this is a broad measure of the overall health of an economy.
- The unemployment rate: unemployment affects consumer spending which, in turn, affects economic growth.
- Retail sales data: consumer consumption accounts for the largest part of a country’s GDP so sales data can provide valuable insight into the health of an economy.
- Sentiment surveys: sentiment surveys such as purchasing managers’ indexes (PMIs) can provide insight into a country’s level of economic expansion or contraction.
Debt
A country’s debt levels can also have an impact on demand for its currency. Countries with large debts in relation to their GDP tend to be less attractive to foreign investors. This translates to lower demand for their currencies.
Political stability
Foreign investors tend to seek out politically-stable countries when investing their capital. Political turmoil in a country can result in lower demand for its currency as foreign capital moves to more stable countries.
Tip: The News Feed on eToro’s Currencies page is a great resource for currency information. Here, traders and investors share information that can be very useful when trading currencies.
Developing a currency trading strategy
Before you begin trading currencies, it’s worth taking the time to develop a trading strategy. This is essentially a plan to help you determine when to buy or sell a currency pair at any given time.
Currency trading strategies can be based on fundamental analysis, technical analysis, or a combination of both.
Fundamental vs technical analysis
Fundamental analysis involves looking at all available information that could affect a currency’s strength or weakness. In this form of analysis, traders look at economic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and unemployment data to determine whether a currency is going to rise or fall.
Technical analysis, on the other hand, involves analysing price charts and indicators to predict a currency’s future movements. In this form of analysis, traders focus on chart patterns and trends and use historical price movements to predict future price movements.
3 popular technical analysis strategies
- Trend trading: This strategy aims to capture gains by analysing a currency’s trend. A trend occurs when a currency moves in one direction for a long period of time. Once you have identified the trend, it may be possible to profit from it by trading in the same direction as the trend.
- Support and resistance trading: This strategy aims to capture gains by identifying a currency’s support and resistance levels. Support is the level where the currency’s price finds it difficult to fall below. Resistance is the level where the currency’s price finds it difficult to go above. Once these areas have been identified, it may be possible to profit by placing trades at the area where the currency’s price is likely to reverse.
- Breakout trading: This strategy aims to capture gains by identifying currencies that have broken through established support or resistance levels. Breakouts can be strong signals, especially when confirmed by other technical analysis indicators.
TIP: If you want to learn more about how to trade using technical analysis please visit
the eToro Trading School page where you can register for a free course.
Developing a set of trading rules
After you have determined which form of analysis you will use to trade currencies, the next step is to develop a solid set of trading rules. This will help you maintain discipline and also reduce risk.
This part of your strategy should focus on:
- Position sizing: Determining your optimal position size is an important part of a trading strategy.
- Entry points: Your plan should consist of rules that determine when to enter a long or short position in a given currency pair.
- Exit points: Your plan should also have rules that determine when to exit a long or short position.
- Stop losses: A trading plan should also focus on risk management tools such as stop losses.
There is no single formula for success when it comes to trading currencies. The key is to start with a basic strategy and refine it over time.
Tip: Learning from eToro’s Popular Investors can help you develop a robust currency trading strategy. Many Popular Investors have significant experience trading currencies, and their advice can be invaluable.
Trading currencies with CFDs
There are a number of ways to trade currencies. One of the easiest ways, however, is through Contracts For Difference (CFDs).
CFDs are financial instruments that offer traders and investors the opportunity to profit from the price movements of a security without actually owning the underlying security.
Setting up a CFD trade is straightforward. Here’s all you need to do:
- Choose the currency pair you wish to trade. For example, EUR/USD
- Set up the trade by selecting
Buy or sell, depending on your view of the currency pair
The amount you wish to invest
The leverage you wish to use
Your stop loss and take profit orders - Open the position
The position will remain open until you either close it or it is closed by a stop loss or take profit order, or the expiration of the contract.
Note that when trading currencies with CFDs, you are always quoted two prices – a buy price and a sell price. The difference between the two is the ‘spread.’

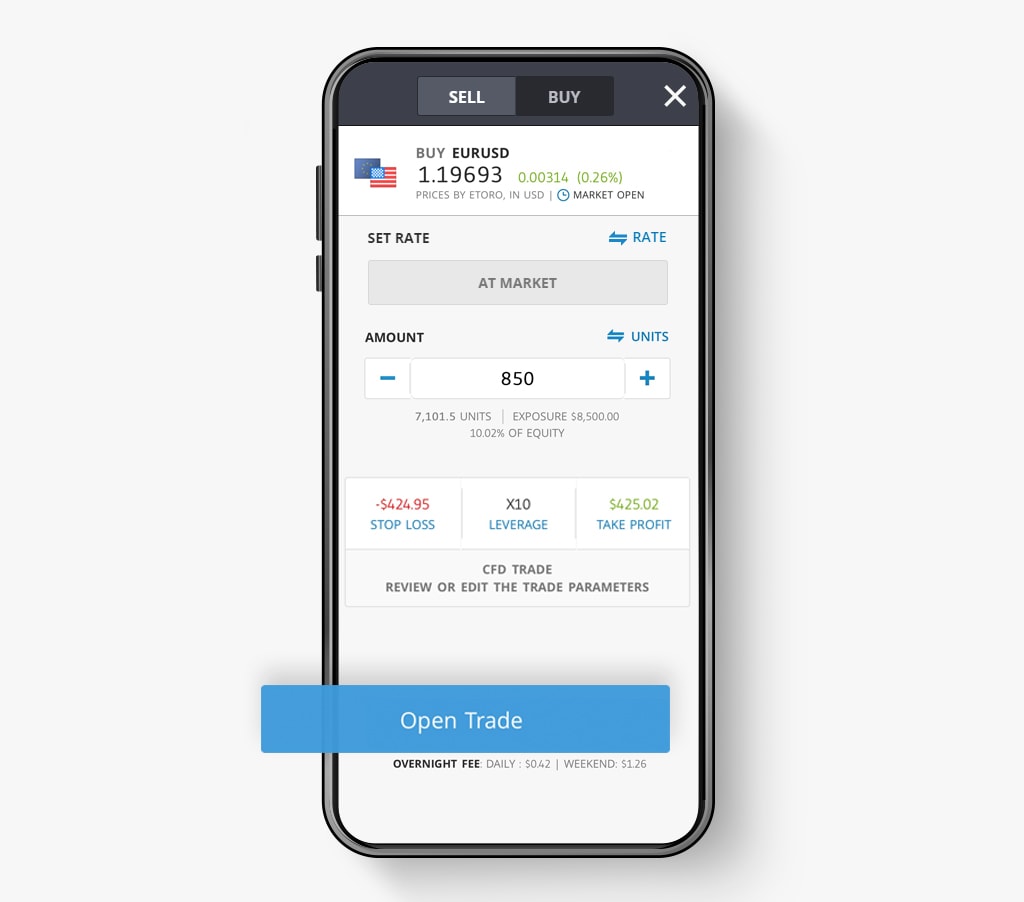
How to place a currency trade on eToro
Placing a currency trade on eToro using CFDs is easy.
Here’s how to do it:
- Login or create an account by clicking here
- Head to our Markets page, and then select Currencies to access the full list of currency pairs
- Select the currency pair that you wish to buy or sell, then select Trade
- Select BUY or SELL depending on the direction you wish to trade
- Enter the amount or number of units you wish to trade
- Set the stop loss, leverage, and take profit parametres
- Select Open Trade
That’s it. It really is very simple.
Risks of currency trading
Any form of investing or trading involves risks and currency trading is no different.
Two of the main risks to be aware of with currency trading are:
- Volatility risk: the foreign exchange market can be highly volatile. While this volatility can create trading opportunities, it can also be a risk factor. Unexpected news can have a significant impact on currency values and unfavourable price movements can result in significant losses for traders. If you do not have sufficient funds in your trading account to cover potential losses, your positions may be closed automatically.
- Leverage risk: while leverage is a powerful tool that can magnify gains, it can also magnify losses. If a large amount of leverage is used to trade, even a relatively small price movement in the wrong direction can result in substantial losses. It’s important to be aware that losses can exceed the amount invested.
Risk management strategies
You can never eliminate risk completely when trading currencies, however, you can reduce it by focusing on risk management.
Two key strategies that can help reduce risk include:
- Determining your optimal position size:before you start trading currencies, you should determine your optimal position size for each trade. A good rule of thumb is to avoid risking more than 2% of your capital on any single trade. Trading more than 2% per trade could expose you to losses that are hard to recover from.
- Putting stop losses in place: stop losses are a fundamental component of a robust risk management strategy. Stop losses help minimise trading losses by closing out losing positions before large losses build up.
Common currency trading mistakes
Like any new skill, currency trading can take time to master. It’s common for beginners to make mistakes while they’re learning.
Here’s a look at four of the most common mistakes novice traders make:
Trading without a strategy
Before placing a trade, it’s important to develop a strategy. This should outline how you will enter and exit both winning and losing trades. If you don’t have a trading strategy, you are increasing your risk.
Ignoring risk management
Risk management is one of the most fundamental parts of a successful trading strategy. Tools such as stop losses help minimise big losses. Having a stop loss for every trade is a sensible move.
Risking too much money on a trade
Many novice currency traders risk more than they can afford to because they don’t understand the basics of position sizing and leverage. By familiarising yourself with these concepts, you’ll reduce the risk of losing more capital than you planned to.
Allowing emotions to dictate a trading strategy
Losses never feel good. However, they are part of currency trading. No trader makes a perfect trade every time. The key is to accept that losses are a normal part of trading and stick to your plan if you experience a loss. Don’t let emotions dictate your trading strategy.
Tip: Always keep a trading journal when trading currencies. Writing things down will help you learn from your mistakes and improve your trading strategy over time.
Summary
- Currency trading involves buying and selling currencies with the aim of generating profits from currency movements.
- There are many benefits of currency trading. The ability to start with a low amount of capital and trade whenever you want to are two of the main benefits.
- Currencies are driven by a number of factors including interest rates, inflation, economic data, debt, and political stability.
- It’s important to develop a trading strategy before placing a currency trade. Many traders use a combination of fundamental analysis and technical analysis when trading currencies.
- CFDs are one of the easiest ways to trade currencies.
- There are risks associated with currency trading. Two main risks include leverage risk and volatility risk.
- Currency trading can take time to master. Mistakes that beginners often make include trading without a strategy, ignoring risk management, and risking more than they can afford to.
Glossary

- BASE CURRENCY – the first currency in a currency pair
- CONTRACT FOR DIFFERENCE (CFD) – A financial instrument that enables you to profit from the price movements of a security without actually owning the underlying security
- COUNTER CURRENCY – the second currency in a currency pair
- CURRENCY PAIR – a quotation for two different currencies
- FOREX – short for foreign exchange. The exchange of one currency for another
- GOING LONG – buying a security
- GOING SHORT – selling a security
- LEVERAGE – using capital borrowed from a broker when opening a position to increase the potential return of an investment
- PIP – the smallest move a currency can make
- POSITION SIZING – determining the optimal size for a trade
- RISK MANAGEMENT – focusing on risk when trading in order to minimise losses
- SPREAD – the difference between the buy and the sell price. This is also the cost of placing the trade
- STOP LOSS – an order designed to minimise losses
- TAKE PROFIT – an order to close a trade at a certain profit level
Get started on eToro to learn more about currencies trading
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any financial instruments.
This material has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and has not been prepared in accordance with the legal and regulatory requirements to promote independent research. Not all of the financial instruments and services referred to are offered by eToro and any references to past performance of a financial instrument, index, or a packaged investment product are not, and should not be taken as, a reliable indicator of future results.
eToro makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this guide. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose.
