In collaboration with
iShares by BlackRock, a global leader in ETFs
ETFs allow you to easily diversify your portfolio, providing access to different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, commodities and real estate. There are many different types of ETFs available to invest in, including active and index ETFs, stock ETFs, bond ETFs, commodity ETFs, international ETFs, and thematic ETFs.
Learn about the different types of ETFs — including stock, bond, thematic, and more — in this beginner’s guide.
Exchange-traded-funds, or ETFs, are an investment product that can provide an easy, low-cost way to get exposure to broader markets or specific sectors. ETFs typically seek to track the performance of a financial index and can be purchased at any point during the trading day.
Want to invest in ETFs but don’t know where to start? In this guide, we will broadly categorize different ETFs and explore the advantages of each one.
Active and index ETFs
Active ETFs, which seek to outperform an index, are managed by professional investors who pick and choose individual stocks, bonds, and other asset classes to include in the fund. This can lead to higher fees, but potentially higher returns.
Active ETFs may be best suited for investors who are looking to generate higher returns in a relatively short amount of time.
On the other hand, index ETFs seek to simply track the performance of an index. Index ETFs typically have lower fees and returns that are more in line with the performance of the index or market they seek to track.
Because of their lower fees, index ETFs may be particularly valuable for long-term investors.
Active ETFs
- Potential for short-term higher returns: Active ETFs may employ more flexible investment strategies than index ETFs, allowing them to pursue opportunities based upon short-term changes in the market.
- In-house investment decisions: A team of fund managers develop the investing strategies used in active ETFs, leveraging tools and resources typically not available for average investors.
- Potential for lower long-term returns: There’s a greater chance an active ETF will underperform its benchmark index, as it’s difficult for anyone to outperform the market consistently over a long period of time.
- Higher fees: Active ETFs typically require relatively more management than index ETFs and as a result, tend to charge higher fees.
Index ETFs
- Low cost: Index ETFs require relatively less management than active ETFs, and are generally more affordable.
- Potential for long-term higher returns: For instance, over a ten-year period ending December 2022, index-tracking strategies, such as those used by a majority of ETFs, have delivered better long-term returns than active strategies. 1
Inflexible investment strategy: Because index ETFs seek to replicate the performance of an index, they typically don’t deviate from the index’s criteria, and may be unable to take advantage of profitable short-term market opportunities.
1 Source: Morningstar. “Morningstar’s U.S/ Active/Passive Barometer. Pg. 2. https://assets.contentstack.io/v3/assets/blt4eb669caa7dc65b2/bltf38c1fd138e35c1e/63fcddc6fac83410ca2abf54/APB_US_2022_Year-End.pdf
Stock ETFs
A stock ETF provides investors with exposure to a diversified portfolio of stocks without having to purchase each one individually. These ETFs are traded on an exchange, and means investors can buy and sell ETF shares throughout the day, just like individual stocks.
A stock ETF may be best suited for investors looking to grow their money without the cost and effort of investing in a bunch of individual stocks.
Stock ETFs can also provide exposure to specific kinds of stocks. For example , a dividend ETF is a type of stock ETF that can provide exposure to stocks that pay dividends. Dividend ETFs may be suited for investors who are looking for consistent income.
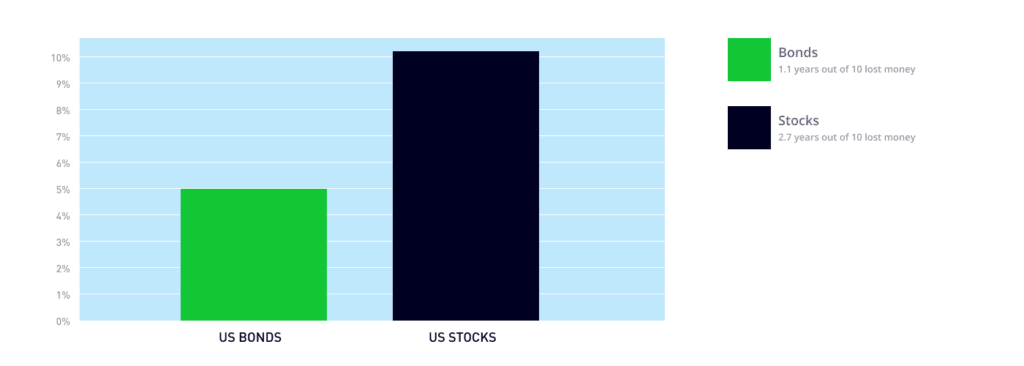
- Higher potential long-term returns: Over the long term, stocks have historically risen higher than other assets, such as bonds, making them a great option to pursue long-term financial goals (see chart below).2
- Targeted exposure to stocks: Stock ETFs may offer exposure to certain types of stocks, such as dividend stocks, so that you do not need to find and purchase each of these types of stocks on your own.
Risky: Stocks historically experience more volatility than other asset classes, such as bonds, which makes investing in stock ETFs riskier than some other investments. 2
2Source: Morningstar, BlackRock. Stocks are represented by the S&P 500 index from 3/4/57 to 12/31/22 and the IA SBBI US large stock index from 1/1/26 and 3/4/57. US bonds are represented by the Bloomberg US Agg Bond TR index from 1/3/89 to 12/31/22 and the IA SBBI US Gov IT index from 1/1/26 to 1/3/89. Past performance does not guarantee or indicate future results. Index performance is for illustrative purposes only. You cannot invest directly in an index.
Stock vs bond returns since 1926
Bond ETFs
Bond ETFs offer exposure to a bundle of bonds you can buy and sell like stocks.
By holding a bunch of bonds, bond ETFs limit the impact of the negative performance of a single bond on the value of your overall investment. Bonds have also historically risen during stock market sell-offs, which could provide additional portfolio protection.
Returns of the Bloomberg US Aggregate Bond Index during market sell-offs
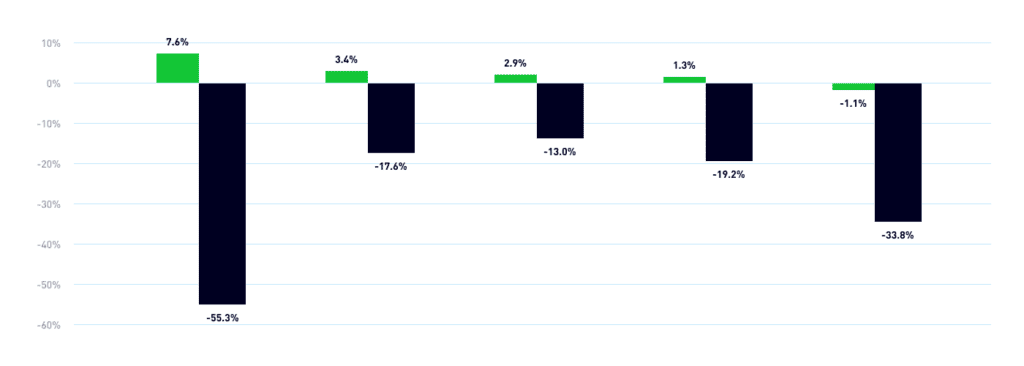
2Source: Morningstar. Financial Crisis measured 10/10/07 – 3/9/09, US Credit Rating Downgrade measured 7/25/11 – 10/3/11, Energy and EM Downturn measured 7/21/15 – 2/11/16, Fed Policy Reaction measured 10/3/18 – 12/24/18, COVID-19 Crisis measured 2/20/20 – 3/23/20. Diversification and asset allocation may not protect against market risk or loss of principal. Index performance is for illustrative purposes only. Index performance does not reflect any management fees, transaction costs or expenses. Indexes are unmanaged and one cannot invest directly in an index. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Index performance is for illustrative purposes only. Index performance does not reflect any management fees, transaction costs or expenses. Indexes are unmanaged and one cannot invest directly in an index. Past performance does not guarantee future results.Performance data represents past performance and does not guarantee future results.
- Accessibility: Bond ETFs offer you exposure to bonds, which can be relatively difficult and expensive for investors to access on their own.
- Stability: Bonds are historically less risky and offer steadier returns than stocks, which could help stabilize your portfolio.
- Potential consistent income: Bonds ETFs offer the potential for investors to earn monthly income, in the form of regular interest payments
- Flexibility: You can buy and sell bond ETFs on an exchange, making them more liquid and accessible than standard bonds.
- Lower potential long-term returns: Historically, bonds have delivered lower long-term returns than stocks, which means you may not grow your money as quickly as with stock ETFs.
- No guarantee of receiving your initial investment back: When an individual invests in a bond, they typically receive back the amount they invested once the bond matures. When an individual invests in a bond ETF, they are not guaranteed to receive their initial investment back.
Similar to stock ETFs, bond ETFs can provide exposure to specific kinds of bonds and as Karen Veraa, Head of iShares US Fixed Income Strategy, notes, “bond ETFs can be a low-cost way for you to potentially boost your portfolio income.”
“Bond ETFs can be a low-cost way for you to potentially boost your portfolio income.”
– Karen Veraa, US Head of Fixed Income Strategy at iShares
For instance, a Treasury ETF provides exposure to bonds issued by the US federal government. These ETFs may be best suited for investors with a relatively lower risk tolerance, as bonds issued by the US federal government are generally viewed as less risky than other investments.
Another type of bond ETF is a high-yield bond ETF, which provides investors with exposure to high-yield bonds, or bonds issued by less creditworthy businesses or governments.
High-yield bonds typically offer investors the potential for higher returns, and might be best suited for investors with a relatively higher risk tolerance.
Commodity ETFs
Commodity ETFs give investors the ability to diversify their portfolios and potentially benefit from price movements in commodities, or physical assets, like gold, oil, and agriculture.
For instance, a gold ETF or silver ETF seeks to track the value of gold and silver.
Commodity ETFs can be used to diversify your investments. Historically, commodities have tended to rise in value when other assets, such as stocks and bonds, fall in value, offering you the potential to earn positive returns when other asset classes experience negative returns.
Commodity ETFs can also be a hedge against inflation, as commodities have tended to rise with inflation.
- Diversification: Commodities have historically risen in value when other assets, such as stocks and bonds, fall in value, adding diversification to your portfolio and serving as a hedge against inflation.
- Offers convenient exposure: Commodity ETFs make it possible to invest in physical assets without having to physically buy or manage them.
Higher volatility: Commodity prices may experience higher levels of volatility than traditional asset classes.
International ETFs
International ETFs offer a great way to invest in companies outside the US and get exposure to foreign markets.
Broad-based international ETFs give investors exposure to global growth. Non-US countries account for 85% of global gross domestic product, and is projected to grow to 90% by 2025. 3
3 PWC, McKinsey Global Institute, as of January 2020. There is no guarantee that forecasts will come to pass.
Some international ETFs offer more precise exposure. For instance, an emerging market ETF offers exposure to stocks in emerging markets, such as India, Brazil, and Mexico. The economies of emerging market countries are projected to become larger than the top seven developed market economies by 2036, and emerging market ETFs can help investors pursue this potential upside. 3
3 PWC, McKinsey Global Institute, as of January 2020. There is no guarantee that forecasts will come to pass.
- Convenience: Investing in international assets can be time consuming and costly, but international ETFs can provide exposure to entire markets in a single trade.
- Diversification: International assets may increase in value during periods when domestic assets may not, helping to stabilize your investments.
Potential volatility: Non-US countries may have different political and economic structures than the United States, which may create additional levels of volatility for your investments.
Thematic ETFs
A thematic ETF is designed to focus on a specific sector or theme, such as environmental sustainability, technology, or healthcare.
A Self-Driving EV and Tech ETF are examples of thematic ETFs which offer exposure to the companies involved in the production and distribution of electric vehicles.
By investing in a thematic ETF, you can put your money into companies that are involved in areas you care about, while still benefiting from the diversification that comes with an ETF.
As Jay Jacobs, US Head of Thematics and Active Equity ETFs at iShares, notes, “Thematic ETFs can provide convenient access to the powerful ideas that may transform our economy.”
“Thematic ETFs can provide convenient access to the powerful ideas that may transform our economy.”
– Jay Jacobs, US Head of Thematics and Active Equity ETFs at iShares
Ability to invest in your interests: A thematic ETF can offer targeted exposure to a certain theme allowing you to focus your portfolio on sectors or causes you feel passionate about.
Risk: Many thematic ETFs invest in relatively small companies, which may increase the volatility of your overall portfolio. There’s also the potential that a specific theme or sector will fizzle out, increasing the chance you could lose your investment.
Conclusion
When it comes to investing in ETFs, you have many options, making it likely you can find an ETF that aligns with your values and financial goals.
Now that you know some of the common types of ETFs, you can start narrowing down your search. Continue to our next lesson to discover how to find the right ETF for you.
About iShares by BlackRock
iShares unlocks opportunity across markets to meet the evolving needs of investors. With more than twenty years of experience, a global line-up of 1300+ exchange traded funds (ETFs) and $3.12 trillion in assets under management as of September 30, 2023, iShares continues to drive progress for the financial industry. iShares funds are powered by the expert portfolio and risk management of BlackRock.
This communication is in collaboration with iShares by BlackRock. BlackRock and iShares are trademarks of BlackRock, Inc. or its affiliates (together “BlackRock”). BlackRock does not sponsor or endorse any content outside the ETF Academy and is not affiliated with eToro or any of its affiliates.
This communication is for information and education purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, a personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to buy or sell, any financial instruments. This material has been prepared without taking into account any particular recipient’s investment objectives or financial situation. Any references to past or future performance of a financial instrument, index or packaged investment product are not, and should not be taken as, a reliable indicator of future results.
eToro encourages its customers to carefully consider the funds’ investment objectives, risks, and charges and expenses carefully before investing. This and other information can be found in the funds’ prospectuses or, if available, the summary prospectuses which may be obtained by visiting each fund company’s website or www.sec.gov/edgar/search. For iShares Funds, please visit www.iShares.com/prospectus. Read the prospectuses carefully before investing.
Investing involves risk, including possible loss of principal. Diversification and asset allocation may not protect against market risk or loss of principal. There can be no assurance that an active trading market for shares of an ETF will develop or be maintained. Transactions in shares of ETFs may result in brokerage commissions and may generate tax consequences. All regulated investment companies are obliged to distribute portfolio gains to shareholders.
Securities trading is offered by eToro USA Securities Inc., member of FINRA and SIPC, a self-directed broker-dealer that does not provide recommendations or investment advice. Visit our Disclosure Library for additional important disclosures including our Customer Relationship Summary and order routing information and statistics. FINRA Brokercheck © 2023.


