Cardano, alongside its native cryptocurrency ADA, has long been one of the world’s most popular blockchains. Learn about the history of Cardano and what sets it apart from its competitors. Find out more about the price of ADA and where it might go in the future.
How does Cardano (ADA) work?
Cardano is a decentralised, third-generation Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain that aims to improve on the flaws of other layer 1 networks, such as Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH).
ADA, named after female mathematician Ada Lovelace, is Cardano’s native utility token, used for settling payments and governing the network. Users who stake Cardano’s cryptocurrency are rewarded with additional ADA for helping to secure the blockchain.
The extensive Cardano ecosystem is overseen by the Cardano Foundation, IOHK and Emurgo. The project is based on peer-reviewed academic research and prioritises openness and transparency.
What makes Cardano different?
First-generation blockchains, such as Bitcoin, did not have the ability to run smart contracts and decentralised applications (dApps). On the other hand, second-generation blockchains, such as Ethereum, struggled to scale their networks.
Cardano is a third-generation blockchain that focuses on scalability and interoperability, which is the ability to connect with other blockchain networks. Cardano also allows developers to create smart contracts.
Cardano is a blockchain platform for changemakers, innovators, and visionaries, with the tools and technologies required to create possibility for the many, as well as the few, and bring about positive global change.
Cardano.org
Cardano and Ethereum are often compared to each other, as the two networks offer similar services within decentralised finance (DeFi). Ethereum is an older, more established network than Cardano, but the blockchain’s expensive gas fees often provides a barrier to entry for retail investors. On the other hand, Cardano has less decentralised applications built on its blockchain, but is a much cheaper and arguably more reliable alternative to Ethereum.
Because of the 5 mentioned above, Cardano’s developers have spent years trying to perfect its offering and are still working on the network’s fundamental functionality. As a result of the developers’ methodological approach, Cardano has never experienced any restarts, shutdowns or outages, unlike some of Cardano’s biggest competitors, such as Solana (SOL).
Tip: “Total Value Locked” (TVL) is a term used to indicate how much money is locked into a particular ecosystem. It is usually a good indication of how many projects are being built on top of a blockchain, and how successful they are.

What is the ADA price and forecast for the future?
ADA, Cardano’s native cryptocurrency, has experienced the same historic, volatile price movements as the wider crypto market.
| Year | Start Price | Mid-Year Price | End Price | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | N/A | N/A | $0.719 | N/A |
| 2018 | $0.719 | $0.138 | $0.041 | -94.30% |
| 2019 | $0.041 | $0.082 | $0.033 | -19.51% |
| 2020 | $0.033 | $0.083 | $0.181 | +448.49% |
| 2021 | $0.181 | $1.384 | $1.310 | +623.76% |
| 2022 | $1.310 | $0.459 | $0.246 | -81.22% |
Prices have been rounded to the nearest three decimal places |Past performance is not an indication of future results
Source: Yahoo! Finance
When comparing ADA’s price year-to-year, it would appear to have less volatility than some other cryptocurrencies. However, between November 2017 and September 2021, ADA’s price rose from $0.025 to $3.099, an increase of 12,296%.
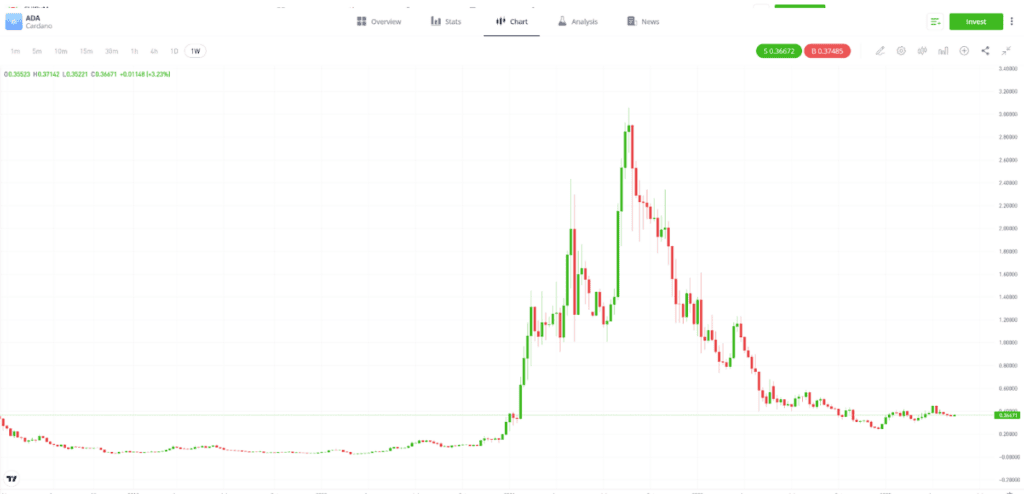
Past performance is not an indication of future results
Source: eToro
It is impossible to predict the future price of ADA, although any price moves have historically been aligned with the price of bitcoin and the rest of the market. ADA has had one of the highest market capitalisations since 2017, and since the Cardano developers are still actively working on the network’s roadmap, many believe that its price will increase over the long term.
However, there are no guarantees, either for Cardano, or within crypto in general, so investors should not invest more than they can afford to lose.
Who created Cardano?
Cardano was launched in 2017 by Ethereum co-founder Charles Hoskinson. Since then, Cardano has followed, and continues to follow, an extensive roadmap of five developmental phases.
| Era | Named After | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Byron | Lord Byron, the father of Ada Lovelace | – The first version of Cardano is launched. – Users can buy and sell ADA using the Ouroboros staking protocol. – Cardano launches the Daedalus and Yoroi cryptocurrency wallets. – ADA is listed on major exchanges. |
| Shelley | Mary Shelley, the author of Frankenstein | – Cardano establishes a decentralised proof of stake consensus model. – Users can delegate ADA to a staking pool, and ADA is distributed to stakers as a reward for helping to secure the network. |
| Goguen | Joseph Goguen, an American computer scientist and academic | – Cardano enables smart contract functionality. – Cardano is designed to be compatible with a range of smart contract languages and platforms, including Plutus. |
| Basho | Matsuo Bashõ, a Japanese poet | – Cardano optimises the network’s speed and interoperability to improve scalability. – Sharding is introduced, which allows computational load to be offloaded to shards or side chains to increase Cardano’s capacity. |
| Voltaire | François-Marie Arouet, a French philosopher and author | – The governance of Cardano is transferred to a decentralised system. – A treasury is introduced. – ADA holders are able to decide on future network developments through a voting system. |
At the time of writing, the Cardano roadmap has not yet been fully completed.
What is Cardano’s Hydra?
In 2023, Cardano deployed a scalability solution called the “Hydra Head Protocol.” Hydra is a layer 2 protocol that operates on top of the Cardano blockchain and is designed to run independently of the main network. Hydra creates multiple “heads,” each of which can process a number of transactions simultaneously, thus increasing Cardano’s transaction per second (tps) speed and reducing transaction fees.

Final thoughts on investing in Cardano
ADA is one of the world’s most popular cryptocurrencies, and despite regular comparisons to Ethereum, Cardano is a blockchain network with its own use cases, fast and affordable transactions, and a growing number of smart contracts being built on top of it. Remember, however, that crypto is an inherently risky asset class, so despite Cardano’s potential, it is important to conduct thorough research before investing in it.
Visit the eToro Academy to learn more about ADA and other cryptocurrencies.
FAQs
- How is ADA created?
-
ADA is primarily distributed through its staking mechanism, which is used to encourage network participants to help secure the growth and safety of the blockchain and its ecosystem. ADA holders stake their tokens by delegating them to a stake pool, earning additional ADA for doing so. There is a maximum supply of 45 billion ADA, much of which was sold to investors or distributed to the Cardano Foundation, Emurgo and IOHK during an initial sales period.
- How do I buy ADA?
-
If you are interested in learning how to buy ADA, there are several methods available. Some investors use a cryptocurrency exchange to swap fiat currency into ADA. Others prefer to use a trading platform that allows them to buy fractional shares of a cryptocurrency, while also giving them access to Copy Trading, Stop-Loss and Take-Profit features.
- What is ADA used for?
-
ADA is primarily used for staking and securing the Cardano network. However, it can also be used for investment purposes, to make purchases or to transact on any one of Cardano’s smart contracts. ADA can also be traded on one of the blockchain’s decentralised exchanges (DEXs).
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any financial instruments.
This material has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and has not been prepared in accordance with the legal and regulatory requirements to promote independent research. Not all of the financial instruments and services referred to are offered by eToro and any references to past performance of a financial instrument, index, or a packaged investment product are not, and should not be taken as, a reliable indicator of future results.
eToro makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this guide. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose.


